DESCRIPTION
For a source of fast neutrons, the neutron-absorbing materials within the shielding are arranged as follows:
They are suitable for activities using neutron emitting sources: nuclear industry, cyclotron, medical accelerator, etc. The wide range of highly hydrogenated matrices (paraffin, polyethylene) loaded with boron or lithium and in brick, plate and cylindrical form can meet special needs in the design phase and during operation.

Paraffin brick
Dimensions (mm): 200 x 100 x 50
Weight: 0.9 kg
| Paraffin | |
|---|---|
| Atomic density of hydrogen/cm³ | 8,13 x 1022 |
| Hydrogen mass % | 14,96% |
| Natural distribution of hydrogen isotopes | 99,98% 1H |
| Density (gr/cm³) | 0,90 |
| Gamma resistance | 106Gy |
| Maximum recommended use temperature | 40°C |
| Melting point | 55°C |
| Colour | Translucent/ white |
| Odour | None |
| Mechanical properties | Mediocre |
| Water absorption | Negligible |
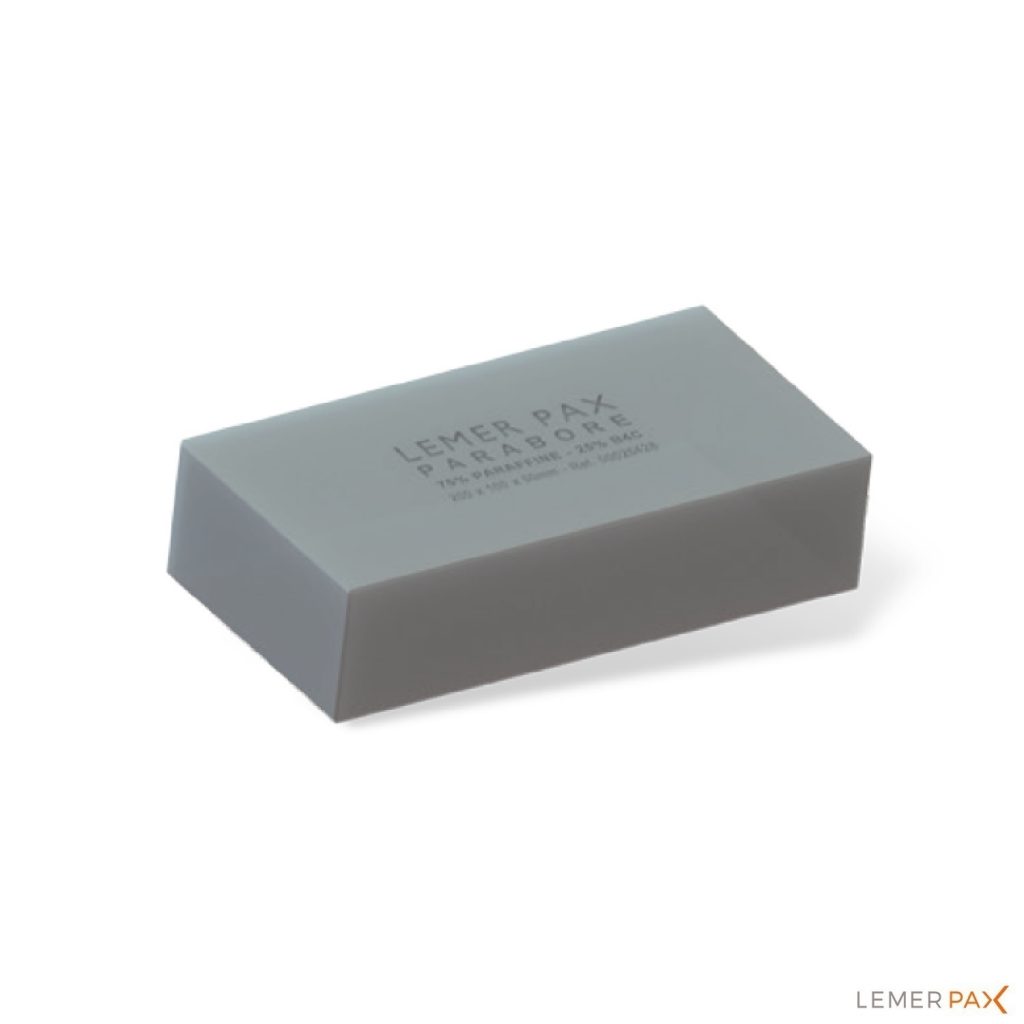

Paraffin brick containing 25% boron
Dimensions (mm): 200 x 100 x 50
Weight: 1.26 kg
| Parabore-25 | |
|---|---|
| Atomic density of hydrogen/cm³ | 6,79 x 1022 |
| Hydrogen mass % | 9,72% |
| Natural distribution of hydrogen isotopes | 99,98% 1H |
| Atomic density of boron/cm³ | 1,6 x 1022 |
| Natural distribution of boron isotopes | 19,6% 10B 80,4% 11B |
| Boron mass % | ≥ 25% |
| Density (gr/cm³) | 1* |
| Gamma resistance | 106Gy |
| Maximum recommended use temperature | 40°C |
| Melting point | 55°C |
| Colour | Dark grey / black |
| Odour | None |
| Mechanical properties | Mediocre |
| Water absorption | Negligible |
Hydrogen-rich polyethylene in plate, brick, or cylindrical form
| Polyethylene | |
|---|---|
| Atomic density of hydrogen/cm³ | 7,90 x 1022 |
| Hydrogen mass % | 13,38% |
| Natural distribution of hydrogen isotopes | 99,98% 1H |
| Density (gr/cm³) | 0,93 |
| Macroscopic crosssection of thermal neutrons | 0,03 cm-1 |
| Gamma resistance | 5 x 106Gy |
| Neutron resistance | 2,5×1017 n/cm² |
| Maximum recommended use temperature | 80°C |
| Melting point | 135°C |
| Colour | White |
| Odour | None |
| Mechanical properties | Excellent |
| Water absorption | Negligible |
Polyethylene containing 5% boron in plate, brick, or cylindrical form
| Polybore-5 | |
|---|---|
| Atomic density of hydrogen/cm³ | 7,48 x 1022 |
| Hydrogen mass % | 11,7% |
| Natural distribution of hydrogen isotopes | 99,98% 1H |
| Atomic density of boron/cm³ | 2,99 x 1021 |
| Natural distribution of boron isotopes | 19,6% 10B 80,4% 11B |
| Boron mass % | ≥ 5% |
| Density (gr/cm³) | 1,07 |
| Macroscopic cross section of thermal neutrons | 2,28 cm-1 |
| Gamma resistance | 5 x 106Gy |
| Neutron resistance | 2,5×1017 n/cm² |
| Maximum recommended use temperature | 80°C |
| Melting point | 135°C |
| Colour | White |
| Odour | None |
| Mechanical properties | Excellent |
| Water absorption | Negligible |
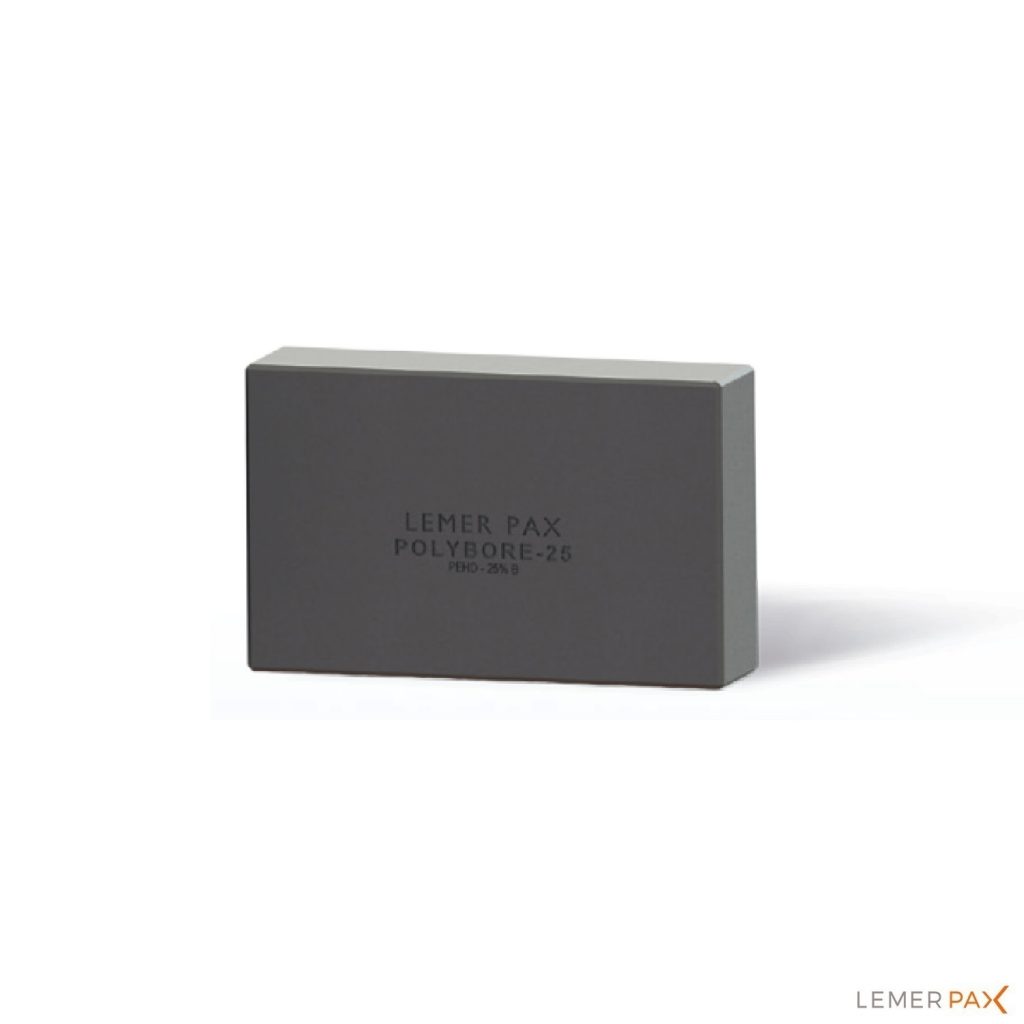

Polyethylene containing 25% boron in plate, brick, or cylindrical form
| Polybore-25 | |
|---|---|
| Atomic density of hydrogen/cm³ | 6,55 x 1022 |
| Hydrogen mass % | 9,3 % |
| Natural distribution of hydrogen isotopes | 99,98% 1H |
| Atomic density of boron/cm³ | 1,6 x 1022 |
| Natural distribution of boron isotopes | 19,6% 10B 80,4% 11B |
| Boron mass % | ≥ 25% |
| Density (gr/cm³) | 1,17 |
| Macroscopic cross section of thermal neutrons | 15,5 cm-1 |
| Gamma resistance | 5 x 106Gy |
| Neutron resistance | 2,5×1017 n/cm² |
| Maximum recommended use temperature | 80°C |
| Melting point | 135°C |
| Colour | Dark grey / black |
| Odour | None |
| Mechanical properties | Excellent |
| Water absorption | Negligible |

Polyethylene containing 7.5% lithium in plate, brick, or cylindrical form
| Polythium-7 | |
|---|---|
| Atomic density of hydrogen/cm³ | 5,44 x 1022 |
| Hydrogen mass % | 8,59 % |
| Natural distribution of hydrogen isotopes | 99,98% 1H |
| Atomic density of lithium/cm³ | 6,96 x 1021 |
| Natural distribution of lithium isotopes | 92,6% 7Li 7,4% 6Li |
| Lithium mass % | 7,56 % |
| Density (gr/cm³) | 1,06 |
| Macroscopic cross section of thermal neutrons | 0,51 cm-1 |
| Gamma resistance | 5 x 106Gy |
| Neutron resistance | 2,5×1017 n/cm² |
| Maximum recommended use temperature | 80°C |
| Melting point | 135°C |
| Colour | White |
| Odour | None |
| Mechanical properties | Excellent |
| Water absorption | Negligible |
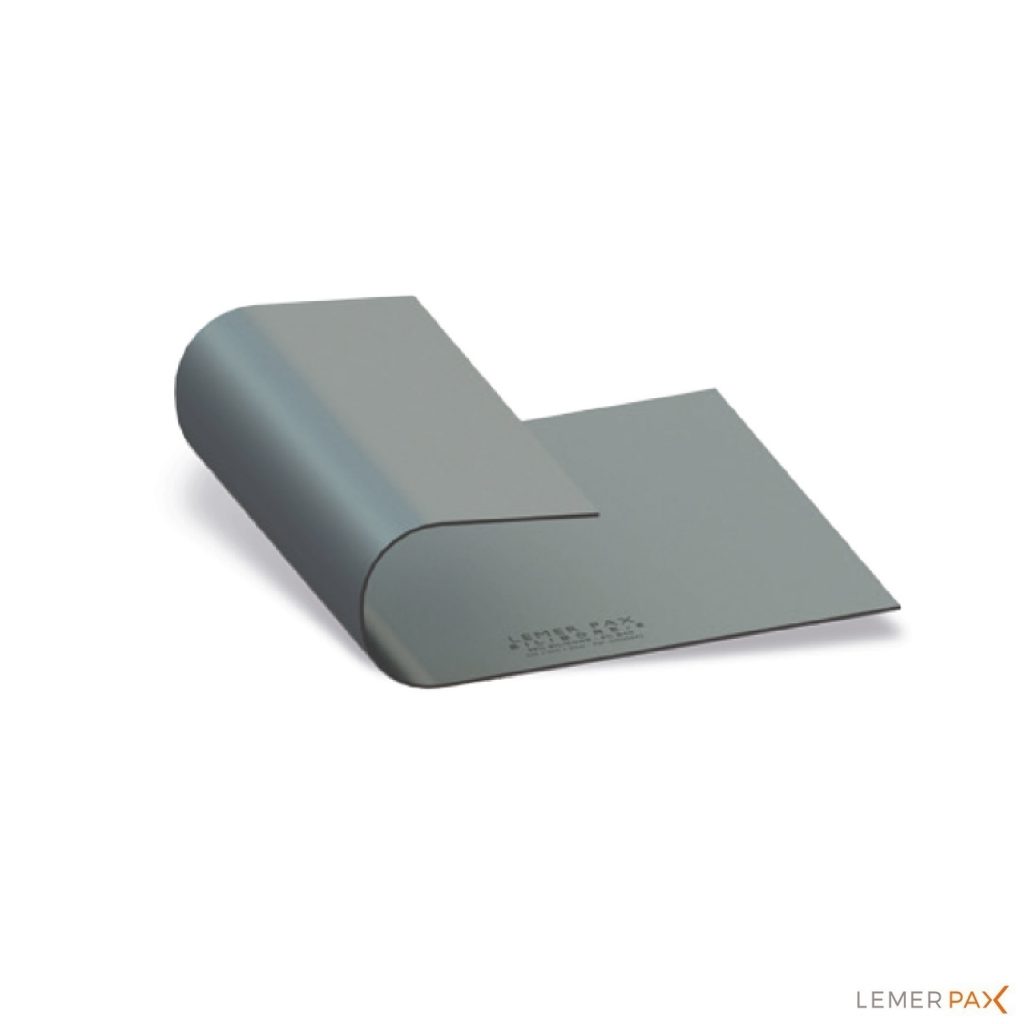

Flexible silicone sheet containing 5% boron
| Silibore-5 | |
|---|---|
| Atomic density of hydrogen/cm³ | 6,62 x 1022 |
| Hydrogen mass % | 7,5 % |
| Natural distribution of hydrogen isotopes | 99,98% 1H |
| Atomic density of boron/cm³ | 0,4 x 1022 |
| Natural distribution of boron isotopes | 19,6% 10B 80,4% 11B |
| Boron mass % | ≥ 5% |
| Density (gr/cm³) | 1,34 |
| Macroscopic cross section of thermal neutrons | 10,4 cm-1 |
| Gamma resistance | 5 x 106Gy |
| Neutron resistance | 2,5×1017 n/cm² |
| Maximum recommended use temperature | 200°C |
| Colour | Dark grey / black |
| Odour | None |
| Mechanical properties | Low |
| Water absorption | Negligible |
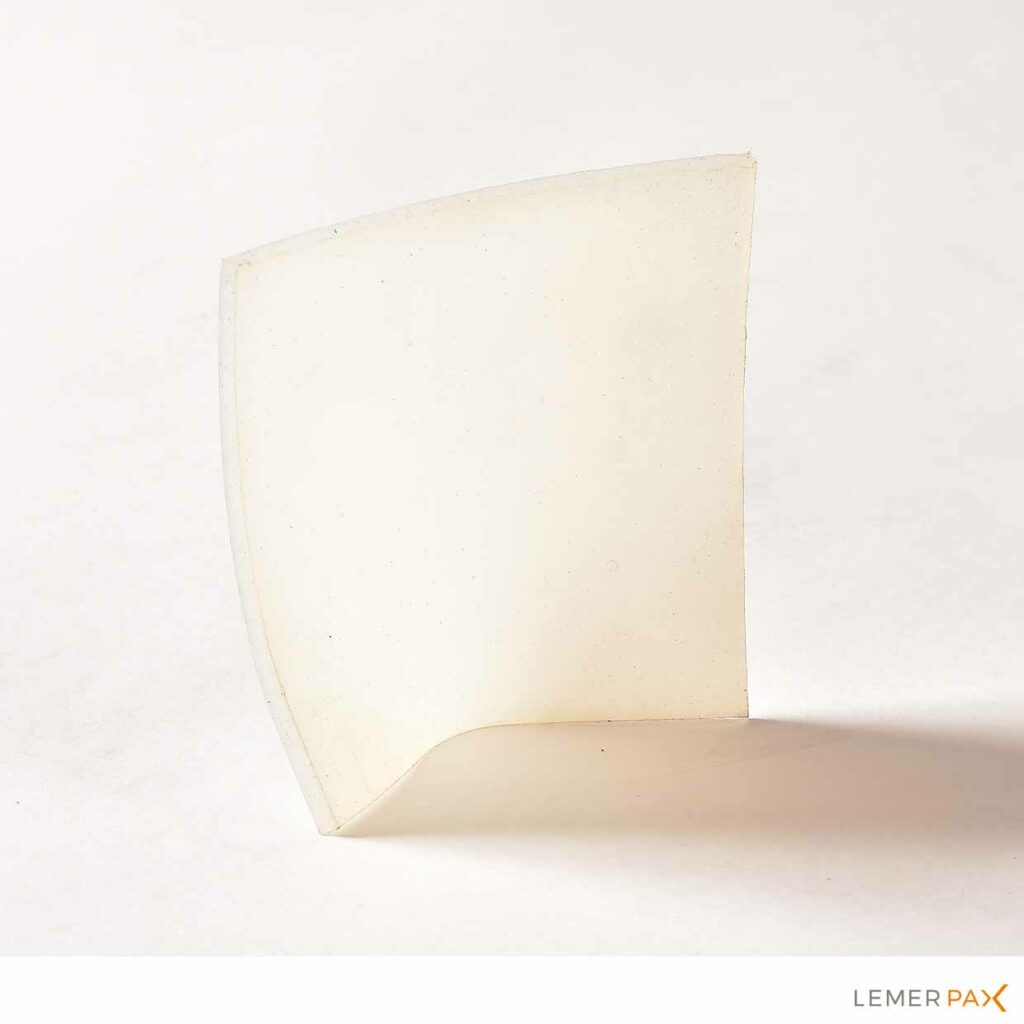

Flexible silicone sheet containing 25% lithium 6
| Silithium-25/79 | |
|---|---|
| Atomic density of hydrogen/cm³ | 5,44 x 1022 |
| Hydrogen mass % | 1,3 % |
| Natural distribution of hydrogen isotopes | 99,98% 1H |
| Atomic density of lithium/cm³ | 6,96 x 1021 |
| Natural distribution of lithium isotopes | 21 % 7Li 79 % 6Li |
| Lithium mass % | 25 % |
| Density (gr/cm³) | 2,25* |
| Gamma resistance | 5 x 106Gy |
| Neutron resistance | 2,5×1017 n/cm² |
| Maximum recommended use temperature | 200°C |
| Colour | White |
| Odour | None |
| Mechanical properties | Low |
| Water absorption | Negligible |
CHARACTERISTICS
ADDITIONNAL PRODUCT